Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- How to unlock ariston washing machine
- Pros and cons of LED lighting
- Pulse relay: device and connection
- How to calculate the illumination of a room with LED lamps?
- Plastic box - do-it-yourself aesthetic view of electrical wiring
- Electricity consumption of a warm floor: electric and film
- Installing a pump in a well: how to properly install pumping equipment
- Electrician Toolkit Overview
- How to choose a water heater: the most complete list of evaluation criteria
- 1 acoustics on the example of Sven SPS-860 and Realtek ALC889 codec
Advertising
| Surge protection device: application and installation diagram |
|
If your home has a lot of expensive household appliances, it is better to take care of organizing a comprehensive protection of the power grid. In this article, we will talk about surge protection devices, why they are needed, what they are and how they are installed. The nature of surge voltages and their impact on technologySince childhood, many have been familiar with the fuss of disconnecting household electrical appliances from the network at the first sign of an impending thunderstorm. Today, the electrical equipment of urban networks has become more advanced, which is why many people neglect elementary protection devices. At the same time, the problem has not completely disappeared; household appliances, especially in private homes, are still at risk. The nature of the occurrence of impulse overvoltages (IP) can be natural and man-made. In the first case, lightning strikes occur due to lightning strikes into overhead power lines, and the distance between the point of impact and consumers at risk can be up to several kilometers. It is also possible to hit radio masts and lightning rods connected to the main ground loop, in which case an induced overvoltage appears in the household network.
Man-made IP are unpredictable, they arise as a result of switching overloads at transformer and distribution substations. With an asymmetric increase in power (only in one phase), a sharp jump in voltage is possible, it is almost impossible to foresee this. Impulse voltages are very short in time (less than 0.006 s), they appear systematically in the network and most often pass unnoticed by the observer. Household appliances are designed to withstand surges up to 1000 V, these appear most often. At a higher voltage, the failure of power supplies is guaranteed, and insulation breakdown in the wiring of the house is also possible, which leads to multiple short circuits and a fire. How SPD is arranged and how it worksSPD, depending on the protection class, may have a semiconductor device on varistors, or have a contact arrester. In normal mode, the SPD operates in bypass mode, the current inside it flows through a conductive shunt. The shunt is connected to the protective ground through a varistor or two electrodes with a strictly standardized gap.
During a voltage surge, even a very short one, the current passes through these elements and spreads along the ground or is compensated by a sharp drop in resistance in the phase-to-zero loop (short circuit). After the voltage stabilizes, the arrester loses its capacity, and the device again operates in normal mode.
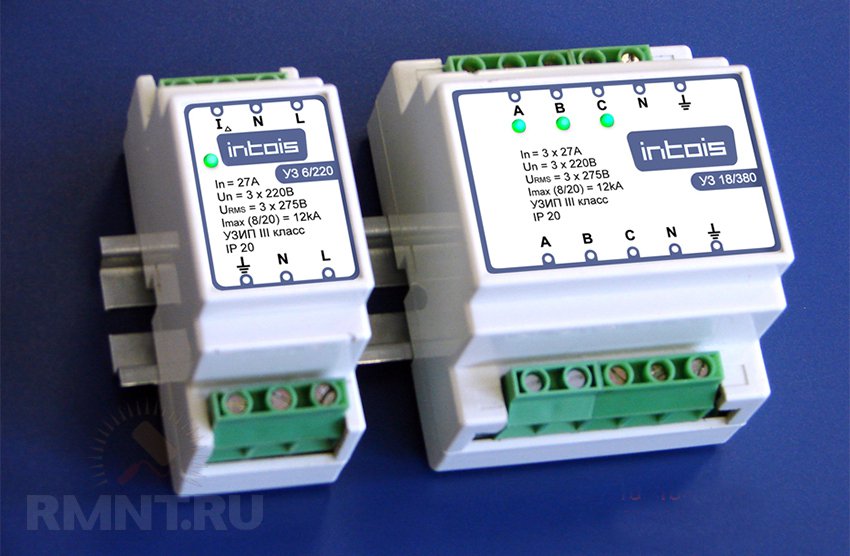
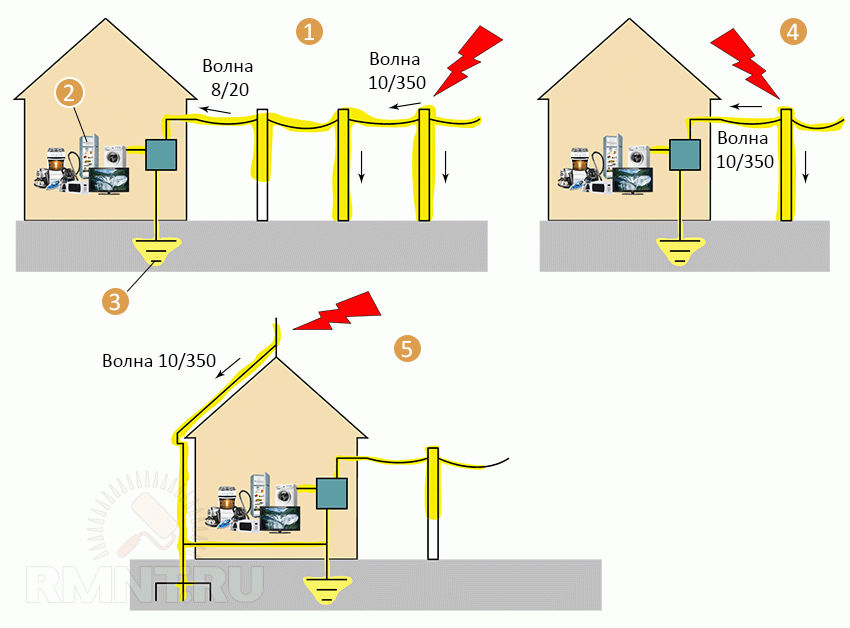
Thus, the SPD closes the circuit for a while so that the excess voltage can be converted into thermal energy. At the same time, significant currents pass through the device - from tens to hundreds of kiloamperes. What is the difference between protection classesDepending on the causes of the occurrence of IP, two characteristics of the increased voltage wave are distinguished: 8/20 and 10/350 microseconds. The first digit is the time during which the IP gains its maximum value, the second is the time it takes to fall to nominal values. As you can see, the second type of overvoltage is more dangerous. Class I devices are designed to protect against IP with a characteristic of 10/350 µs, which most often occur when lightning strikes in power lines closer than 1500 m to the consumer. The devices are capable of briefly passing through themselves a current from 25 to 100 kA, almost all class I devices are based on arresters. SPDs of class II are focused on compensation of IP with a characteristic of 8/20 µs, peak current values in them range from 10 to 40 kA. Protection class III is designed to compensate for overvoltages with current values less than 10 kA with a characteristic IP of 8/20 μs. Protection class II and III devices are based on semiconductor elements.
It may seem that it is enough to install only class I devices, as the most powerful ones, but this is not so. The problem is that the higher the lower threshold of the forward current, the less sensitive the SPD. In other words: with short and relatively low IP values, a powerful SPD may not work, and a more sensitive one will not be able to cope with currents of this magnitude. Protection class III devices are designed to eliminate the lowest SI - only a few thousand volts. They are completely similar in characteristics to protection devices installed by manufacturers in power supplies for household appliances. In case of redundant installation, they are the first to take on the load and prevent SPD operation in devices, the resource of which is limited to 20-30 cycles. Is there a need for an SPD, risk assessmentA complete list of requirements for the organization of protection against IP is set out in IEC 61643-21, you can determine the mandatory installation according to the IEC 62305-2 standard, according to which a specific assessment of the degree of risk of a lightning strike and the consequences caused by it is established.
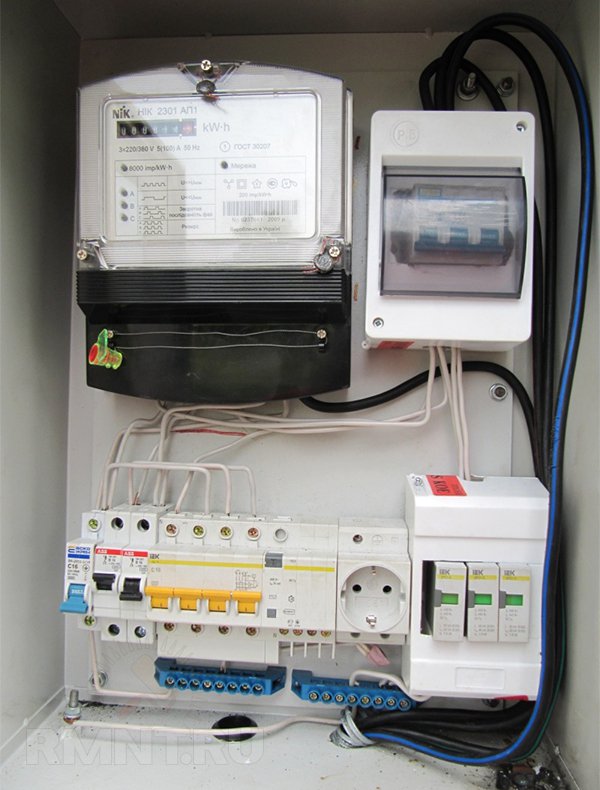
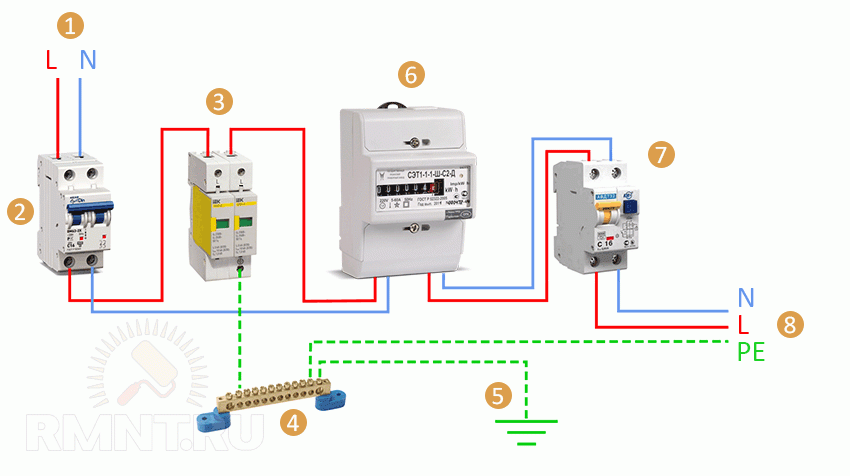
In general, when supplying power from overhead power lines, the installation of a class I SPD is almost always preferable, unless a set of measures has been taken to reduce the impact of thunderstorms on the power supply mode: re-grounding of supports, PEN-conductor and metal bearing elements, a lightning rod device with a separate potential equalization systems. An easier way to assess risk is to compare the cost of unprotected appliances and security devices. Even in multi-storey buildings, where overvoltages are very low with a characteristic of 8/20, the risk of insulation breakdown or failure of devices is quite high. Installation of devices in the main switchboardMost SPDs are modular and can be mounted on a 35mm DIN rail. The only requirement is that the shield for installing the SPD must have a metal case with a mandatory connection to the protective conductor.
When choosing an SPD, in addition to the main performance characteristics, you should also take into account the rated operating current in bypass mode, it must correspond to the load in your mains. Another parameter is the maximum clamping voltage, it should not be lower than the highest value within the daily fluctuations. SPDs are connected in series to a single-phase or three-phase supply network, respectively, through a two-pole and four-pole circuit breaker. Its installation is necessary in case of soldering of the spark gap electrodes or breakdown of the varistor, which causes a permanent short circuit. Phases and a protective conductor are connected to the upper terminals of the SPD, and zero to the lower terminals.
When installing several protective devices with different protection classes, they must be coordinated using special chokes connected in series with the SPD. Protective devices are built into the circuit in ascending order of class. Without coordination, more sensitive SPDs will take on the main load and fail earlier. The installation of chokes can be avoided if the length of the cable line between devices exceeds 10 meters. For this reason, SPDs of class I are mounted on the facade even before the meter, protecting the metering unit from surges, and the second and third classes are installed, respectively, on the ASU and floor / group shields. |
New
- Pros and cons of LED lighting
- Pulse relay: device and connection
- How to calculate the illumination of a room with LED lamps?
- Plastic box - do-it-yourself aesthetic view of electrical wiring
- Electricity consumption of a warm floor: electric and film
- Installing a pump in a well: how to properly install pumping equipment
- Electrician Toolkit Overview
- How to choose a water heater: the most complete list of evaluation criteria
- 1 acoustics on the example of Sven SPS-860 and Realtek ALC889 codec
- Grounding and zeroing: purpose, difference, features