Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- How to unlock the washing machine ariston
- Pros and cons of LED lighting
- Impulse relay: device and connection
- How to calculate the illumination of a room with LED lamps?
- Plastic box - an aesthetic do-it-yourself wiring
- Electricity consumption of underfloor heating: electric and film
- Installing a pump in a well: how to properly install pumping equipment
- Electrician Tool Kit Overview
- How to choose a water heater: the most complete list of evaluation criteria
- 1 acoustics on the example of Sven SPS-860 and Realtek ALC889 codec
Advertising
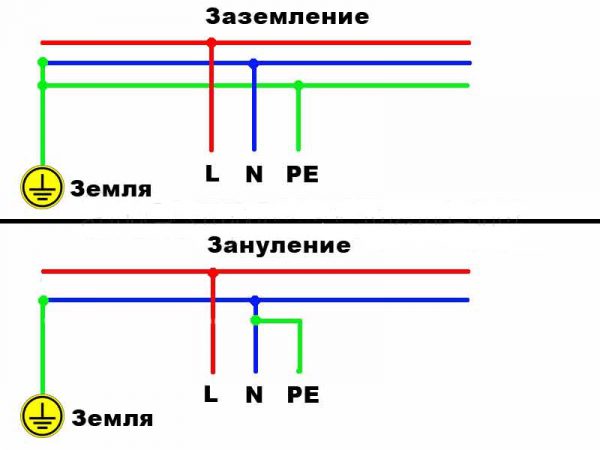
| The main differences between grounding and grounding |
|
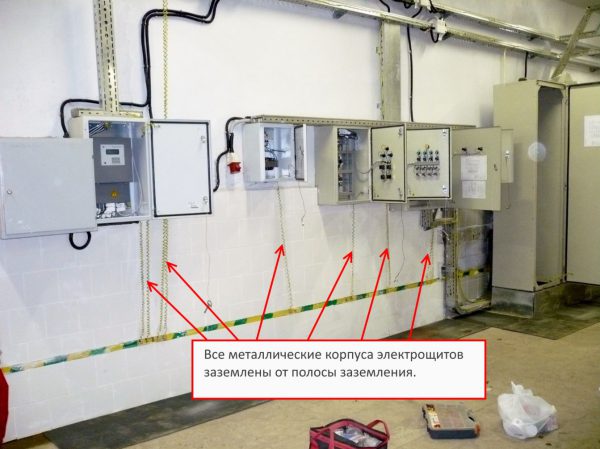
The main requirement for any electrical appliance is operational safety. This is especially true for equipment in contact with water. In the absence of additional protection, even a small problem with the electrical wiring (burn-through of the insulating layer, puncture between the turns of the engine) is dangerous. An electrical potential appears on the body of the faulty device. In this case, a person or an animal touching the body may get an electric shock. To avoid this, protection methods such as neutralization and grounding have been developed. Grounding tasksAn artificially created contact between an electrical installation and the ground is called grounding. Its task is to lower the voltage on the device case to a level that is safe for living beings. In this case, most of the current is diverted into the ground. In order for the grounding system to work effectively, its resistance must be significantly lower than in the rest of the circuit. This requirement is based on the property of the electric current to always choose the smallest resistance on its way.
The fault current is sometimes insufficient when using an earthing switch with a resistance that is relatively high for the reaction of protective devices. Therefore, another task of the grounding system is the growth of the emergency fault current. Types of grounding devices:
Grounding devices are natural and artificial:
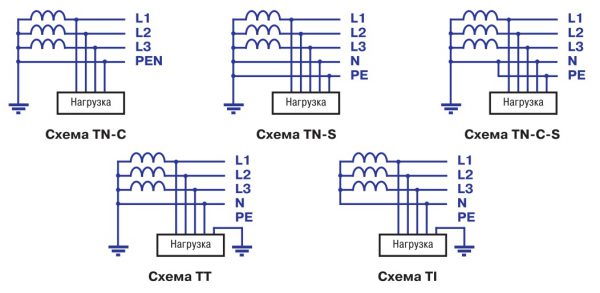
For the grounding system, pipes intended for transporting flammable substances (both gases and liquids), aluminum parts, cable sheaths must not be used. Also, objects covered with an anti-corrosion insulating layer are not suitable for this purpose. It is forbidden to use water and heating pipes as grounding conductors. Technical design of grounding systemsThere are several connection schemes with a different composition of protective and working conductors:
The type of grounding is indicated by the first letter in the designation:
The grounding method for exposed conductors is determined by the second letter:
After the hyphen, there are letters indicating the method of functioning of the protective PE and working N neutral conductors: S - the work of conductors is provided by a single PEN conductor; C - there are several conductors.
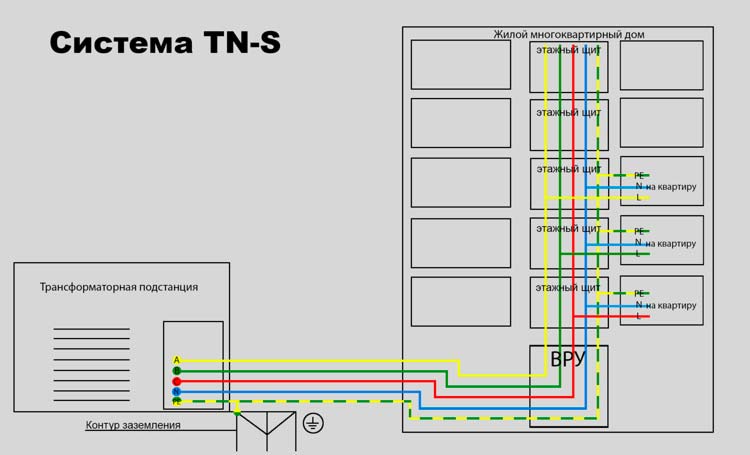
TN systemThe TN-type grounding includes subsystems TN-C, TN-S, TN-C-S. The oldest of these subsystems, TN-C, is used in 3-phase four-wire and 1-phase two-wire power grids. Such networks are usually found in old buildings. For all its simplicity and relatively low cost, the system does not provide a sufficient level of security, and therefore is not used in new buildings. Subsystem TN-C-S is used for renovation of old buildings. It is relevant where the working and protective conductors are combined at the input. The use of TN-C-S is necessary for the reconstruction of the system when computer or telecommunication equipment is installed in the old building. This ground is a transitional type between TN-C and the most modern subsystem - TN-S. TN-C-S is a relatively safe and affordable financial grounding scheme. The difference between the TN-S subsystem from other types of such equipment is the location of the working and neutral conductors. They are installed separately, with the neutral PE conductor uniting all existing conductive elements of the electrical installation. To avoid duplication, create a transformer substation equipped with a main grounding. An additional advantage of the substation is the ability to reduce the length of the conductor running from the cable entry into the equipment to the ground electrode.
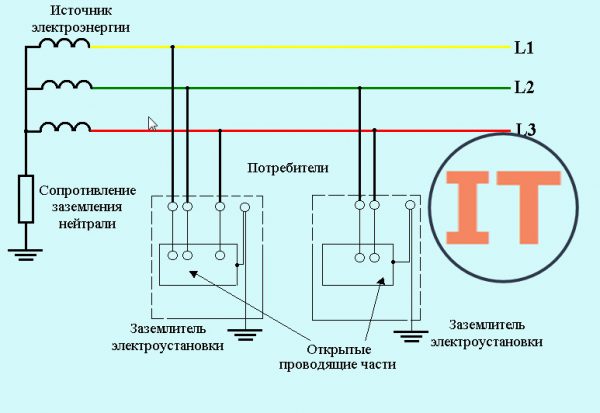
TT systemIn this grounding system, current-carrying open elements are in direct contact with the ground. In this case, the electrodes do not depend on the substation neutral grounding device. TT is used when, for technical reasons, it is impossible to build a TN system. IT systemIn this system, the neutral of the power supply does not touch ground or is grounded by a high impedance installation. The circuit is popular in situations where it is necessary to connect sensitive equipment (hospitals, laboratories, etc.).
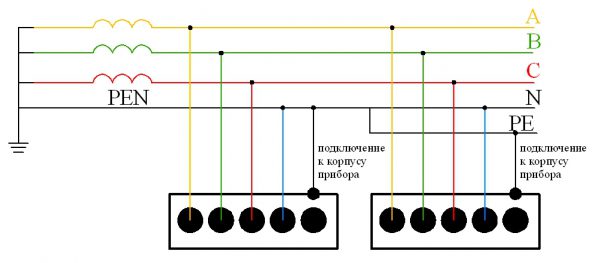
ZeroingThe neutralization process consists in combining non-energized metal elements with the grounded neutral of a 3-phase step-down current source. Also use the grounded terminal of the 1-phase current generator. Zeroing is used to provoke a short circuit in the event of a breakdown of the insulating layer or penetration of current into a non-current-carrying equipment element. The meaning of the short circuit is that after that the circuit breaker is triggered, the fuses are blown out, or other protective means are turned on. Zeroing is used in electrical installations with solidly grounded neutral.
When installing grounding, it should be borne in mind that a short circuit should lead to melting of the fuse or disconnection of the circuit breaker. If this does not happen, the free flow of the fault current in the electrical circuit will cause a voltage to appear on all zeroed objects, and not only at the breakdown site. The voltage indicator is the product of the zero resistance and the fault current, which is very dangerous when a living creature is struck by current.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the good condition of the neutral conductor. When it is broken, a voltage arises on all zeroed elements, since they automatically come into contact with the phase. For this reason, it is forbidden to install any protective devices on the neutral conductor (in addition to switches and fuses), due to which a break occurs when triggered. To reduce the risk of electric shock when the neutral conductor is broken, additional grounding is created every 200 meters of the line, as well as on the end and input supports. The resistance level on each new earthing switch should not be higher than 30 ohms. Difference between grounding and zeroThe main difference between grounding and earthing is the purpose of the systems. Grounding is necessary to quickly reduce the voltage to an acceptable level. The task of grounding is to completely turn off the current in the area where a breakdown to the case or other non-conductive element has occurred. Zeroing is associated with a decrease in the potential of the housing in the period between closing and disconnecting the electricity supply.
In new buildings, grounding is not used. In new buildings, a 3-wire cable with a phase, neutral and earth (1-phase system) or a 5-wire cable (three phases, neutral and earth) is installed in a 3-phase system. The most commonly used scheme is TN-S, but TN-C-S is also found. Do I need to do grounding in the apartmentIt is not worth using zeroing in order to protect residents and electrical installations in an apartment - there are situations when a refrigerator (or other device) is zeroed, and a current breakdown occurs. Also, incorrectly performed electrical wiring is often found (after all, an electrician could have confused the wires and connected a phase instead of zero). In such cases, household appliances fail even before the circuit breaker is triggered.
Grounding and grounding requirementsAll electrical installations and circuits equipped with neutral conductor insulation require installation of a protective system (neutralization or grounding). There are several rules to follow when creating a security system:
Subject to grounding:
As for housing, grounding and grounding is necessary for electrical household appliances with a capacity of more than 1300 watts. Metal products such as bathtubs and shower trays, suspended ceilings are subject to grounding for potential equalization. A dedicated conductor is used to ground air conditioners, electric stoves or similar electrical consumers with a capacity of more than 1,300 watts. It should be connected to the zero of the mains.
A detailed list of electrical installations requiring protection by grounding or grounding is indicated in the Electrical Installation Rules. PUE is an official document, it contains all the standards. The document also establishes a list of equipment for which protection is optional. The creation of a grounding and grounding system is extremely important, the safety of people and the preservation of property depend on it. Therefore, the cost of a mistake is high. It is recommended that only qualified workers be assigned this work. |
New
- Psychology of educational activity of a younger student. Psychological foundations of teaching a younger student.
- Introduction to the specialty
- Introduction to the specialty
- The psychology of teaching a younger student
- The transition to NEP and repression against dissent 20 30 years of the USSR
- Moscow State University of Press Features of the use of impersonal predicative words
- Responsibility falls on the shoulders of the farmer
- Keynesian model of macroeconomic equilibrium ("Keynesian cross")
- Business game "manager's work week"
- Moscow State University of Printing Arts Computer networks are not used